NGC 3372 - The Eta Carinae Nebula
The Eta Carinae Nebula is a giant nebula 9000 light years from us in the Sagittarius Arm of the Galaxy. Although it is a large distance from us, the central region of this nebula is bright enough to see with the naked eye (although only from equatorial and southern latitudes on Earth). The vivid colours seen in pictures of nebulae usually only appear on photographs, the human eye is not very sensitive to dim colours, and so with the naked eye a nebula such as the Eta Carinae Nebula only appears to be white.
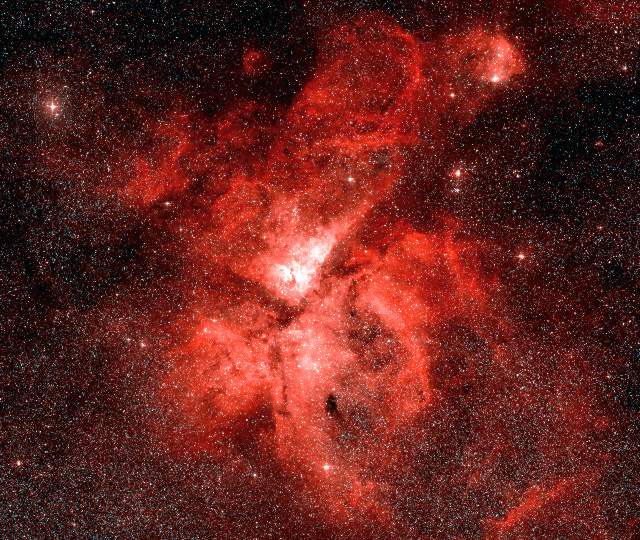

The Eta Carinae Nebula. Image size: 3.0°x2.5°. DSS image. © AAO/ROE
The Nebulae associated with the Eta Carinae Nebula
The Eta Carinae nebula is classified as NGC 3372, it covers about three degrees of the sky which at a distance of 8800 light years corresponds to a diameter of about 460 light years. Two other nebulae have been added to the list below, but they are probably neighbouring nebulae not connected to the Eta Carinae nebula. They have very uncertain distances but they are probably also in the Sagittarius Arm.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Catalogue Equatorial Galactic Size Type Distance Size Other Names
Number Coordinates Coordinates (arcmins) (ly) (ly)
RA (2000) Dec l° b°
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NGC 3199 10 17.4 -57 55 283.6 -0.9 22' E 7000? 45?
NGC 3372 10 45.1 -59 52 287.7 -0.8 180' E 8800 460 Eta Carinae Nebula
NGC 3503 11 01.3 -59 51 289.5 +0.1 3' E 10000? 10?
|
Column 1: The standard catalogue name for the nebula.
Column 2: Right Ascension and Declination for epoch 2000.
Column 3: Galactic Longitude (l) and Latitude (b).
Column 4: Angular size of the nebula in arcminutes.
Column 5: Nebula type: E = emission, R = reflection.
Column 6: Approximate distance to the nebula.
Column 7: Approximate size of the nebula in light years.
Column 8: Alternative name of the nebula.
Star clusters associated with the Eta Carinae Nebulae
There a lot of star clusters in the vicinity of the Eta Carinae nebula. Many of them are probably foreground clusters in front of the nebula. Two of these clusters are definitely within the nebula - Trumpler 14 and Trumpler 16. Trumpler 16 includes the star Eta Carinae as one of its member stars.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Catalogue Equatorial Galactic Size Distance Age Other Names
Name Coordinates Coordinates (arcmins) (ly) (million
RA (2000) Dec l° b° years)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BH 90 10 11.9 -58 04 283.1 -1.5 4' 8400 88
IC 2581 10 27.5 -57 37 284.6 +0.0 5' 8000 14
NGC 3293 10 35.8 -58 14 285.9 +0.1 6' 7600 10 Gem Cluster
NGC 3324 10 37.4 -58 39 286.2 -0.2 12' 7550 6
Collinder 228 10 42.1 -59 55 287.4 -1.0 14' 7200 7
Bochum 10 10 42.3 -59 08 287.0 -0.3 20' 6600 7
Trumpler 14 10 44.0 -59 33 287.4 -0.6 5' 8900 7
Trumpler 15 10 44.8 -59 22 287.4 -0.4 14' 6050 8
Trumpler 16 10 45.0 -59 43 287.6 -0.7 10' 8700 6 Eta Carinae Cluster
Collinder 232 10 45.0 -59 33 287.5 -0.5 4' 7850 5
Bochum 11 10 47.3 -60 05 288.0 -0.9 21' 7850 6
Ruprecht 92 10 53.8 -61 45 289.5 -2.0 7' 7700 63
Trumpler 17 10 56.5 -59 12 288.7 +0.4 5' 7150 51
Bochum 12 10 57.5 -61 43 289.9 -1.8 10' 7250 41
|
A Map of the Eta Carinae Nebula
Below is a map of the star clusters and nebulae in the region of the Eta Carinae nebula. The Eta Carinae nebula is a large complex nebula with many recently formed stars within it. To the left of the Eta Carinae nebula is a second much fainter (and possibly more distant) nebula around NGC 3503. The name NGC 3503 however, only refers to a tiny bright patch of this nebula.
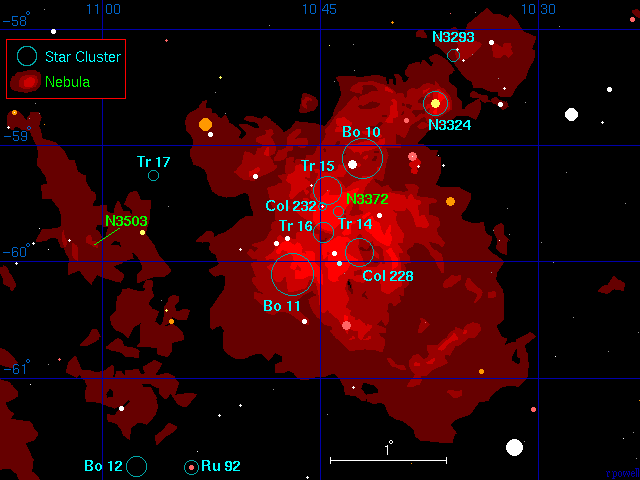
The location of the Eta Carinae Nebula
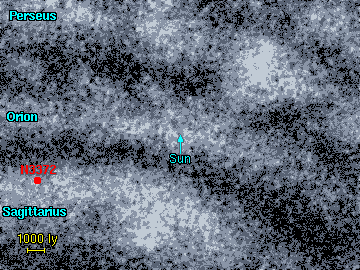 | The distance to the Eta Carinae is known fairly accurately because there are two star clusters buried at the heart of the nebula (Trumpler 14 and Trumpler 16). The nebula is about 8800 light years away and lies in the Sagittarius Arm. The Eta Carinae nebula is an example of the type of giant nebula which could be seen from far above the Galaxy, hundreds of thousands of light years away. |
The Reason Why Emission Nebulae are Red
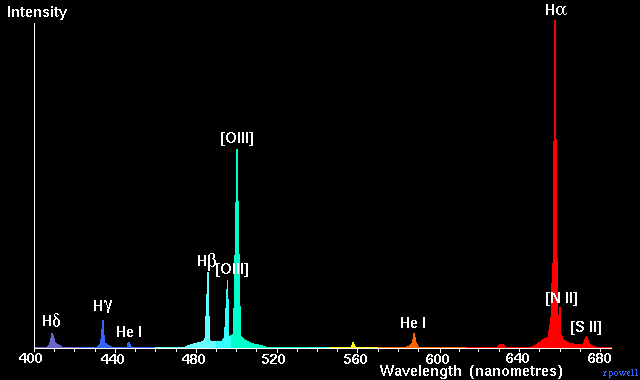
The reason why most bright nebulae are red is because they consist mostly of hydrogen. When hydrogen glows, it emits bright red light. This graph, below, shows the intensity of light from the Eta Carinae Nebula. It is a typical emission nebula spectrum. The strongest emission comes from the red hydrogen-alpha line (at 656 nanometres) although hydrogen also emits some weaker blue light (these are the hydrogen beta, gamma and delta lines at 486nm, 434nm and 410nm).
The only other important optical emission is due to the presence of oxygen - these are the two [OIII] lines at 501nm and 496nm. In planetary nebulae this can often be the strongest source of light and it gives some planetary nebulae a characteristic blue-green colour.
Eta Carinae
In the picture below, the star, Eta Carinae, is shown. It lies next to the 'Keyhole nebula', a dark nebula with a keyhole shape, although it seems likely that the keyhole was darker in the late nineteeth century when it was first named. The star Eta Carinae does not look spectacular although it has brightened slightly since the late nineteeth century and it is now at the limit of naked-eye visibility.
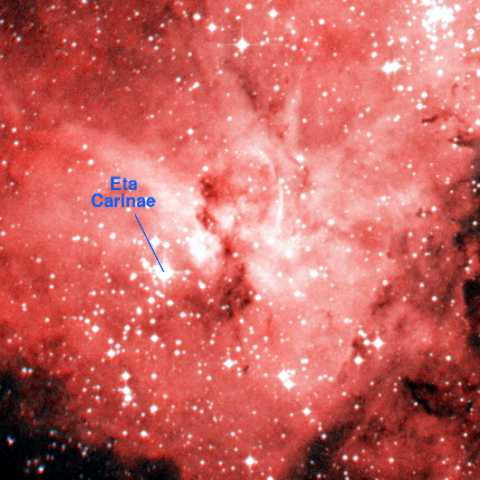

The Keyhole Nebula. Image size: 0.25°x0.25°. DSS image.
| by An Atlas of Universe |

Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário